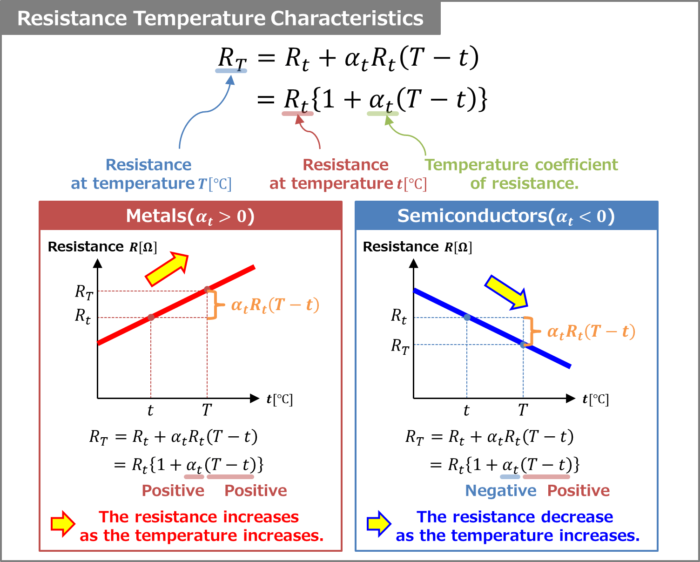
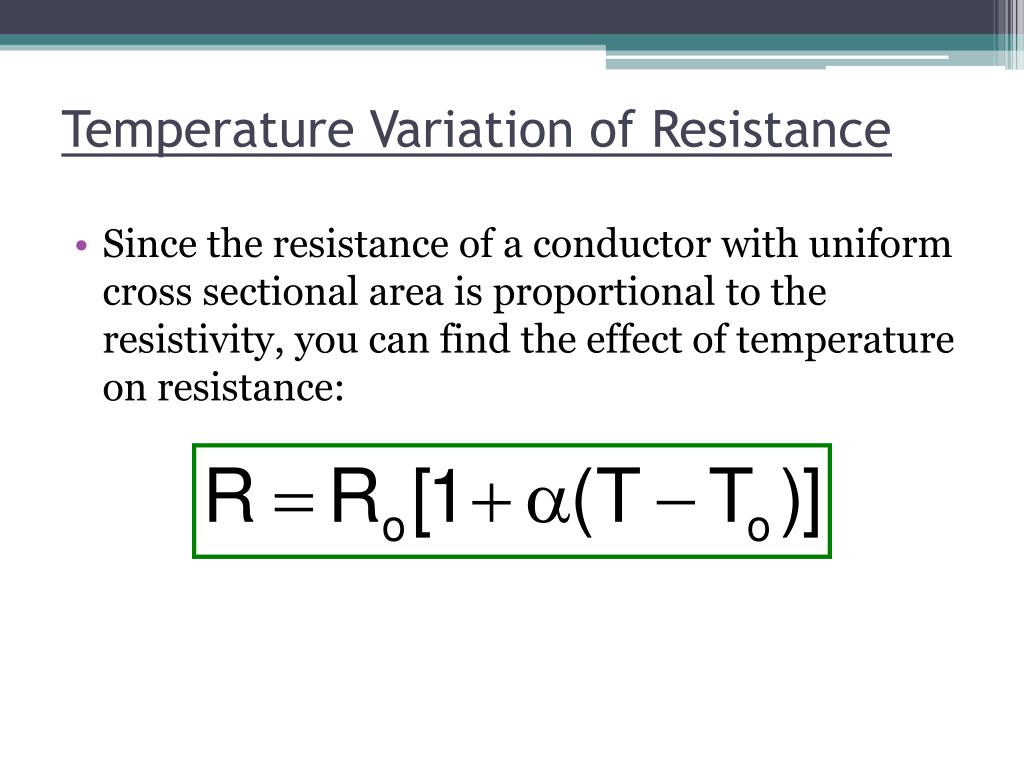
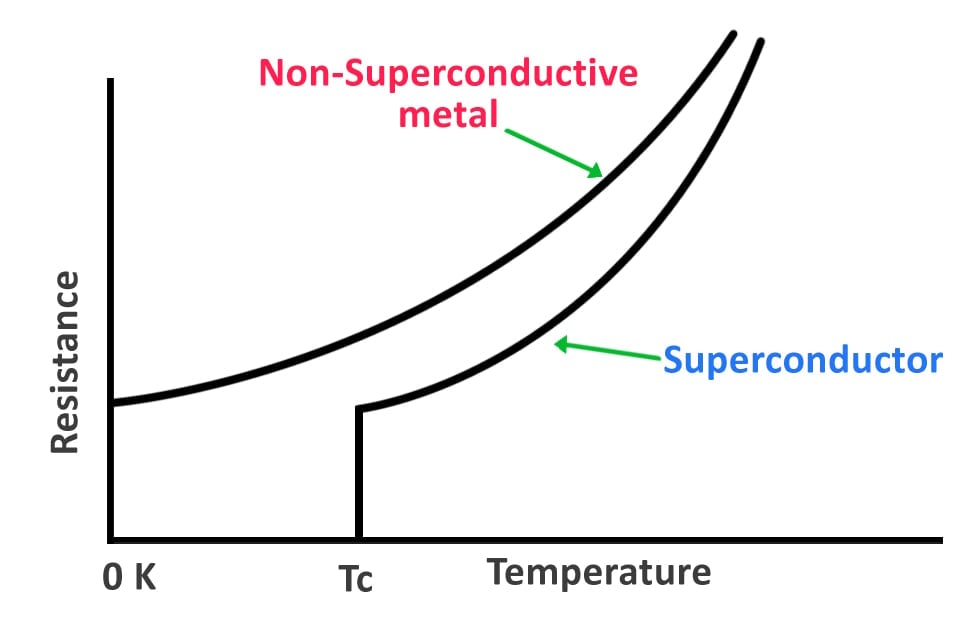
Temperature Variation of Resistance. The resistivity of all materials depends on temperature. Some even become superconductors (zero resistivity) at very low temperatures. (See Figure 20.11.) Conversely, the resistivity of conductors increases with increasing temperature. Since the atoms vibrate more rapidly and over larger distances at higher.. Over relatively small temperature changes (about 100∘C 100 ∘ C or less), resistivity ρ ρ varies with temperature change ΔT Δ T as expressed in the following equation. ρ = ρ0 (1 + αΔT), (8.4.2) (8.4.2) ρ = ρ 0 ( 1 + α Δ T), where ρ0 ρ 0 is the original resistivity and α α is the temperature coefficient of resistivity.
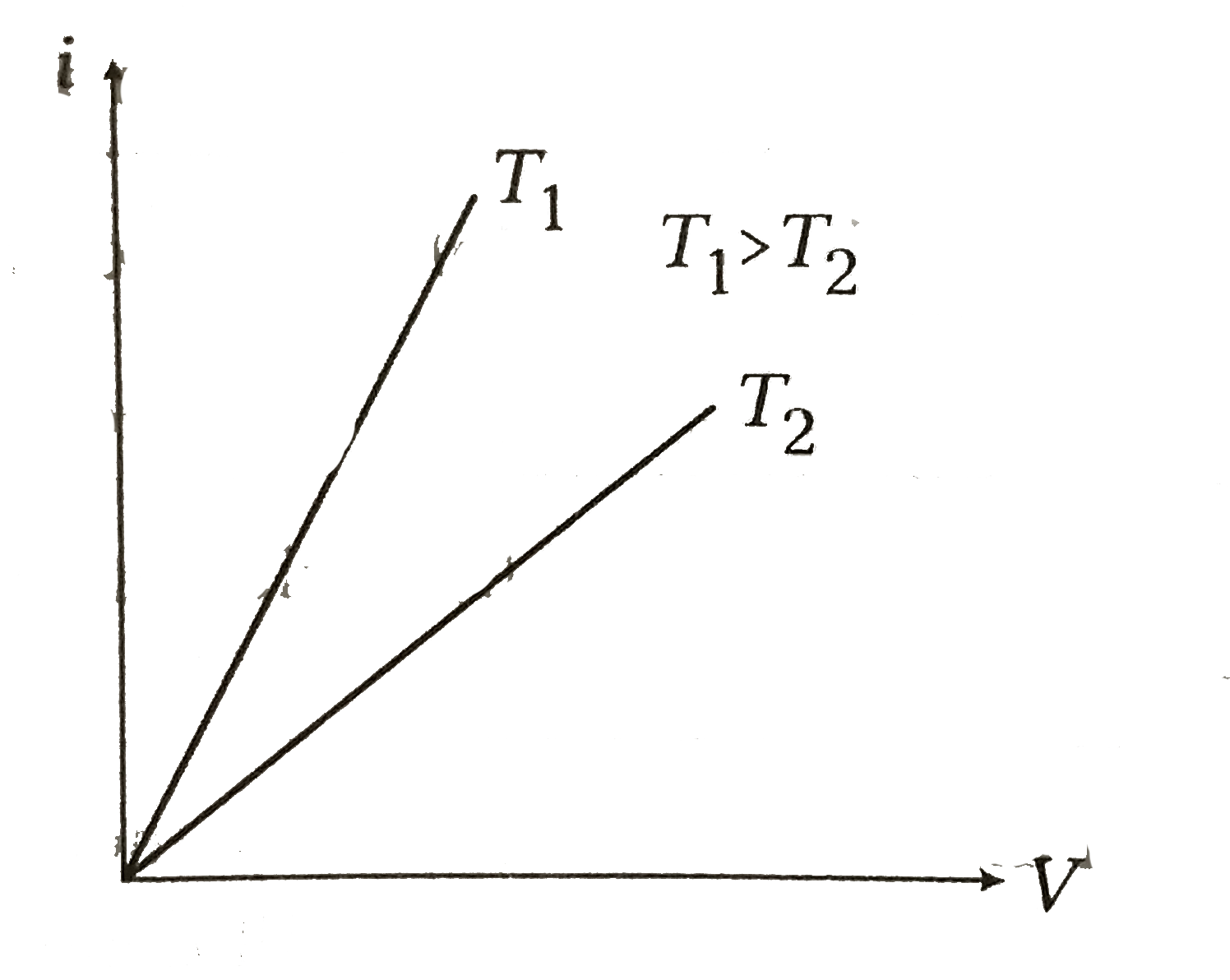
The variation of resistance of a metallic conductor with temperature is
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance Electrical Information

Which of the following graph represents the variation of resistivity
Physics Learn EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON RESISTANCE, GSEB Physics

(a) Variation of resistance as a function of temperature at various

thermodynamics Electrical conductivity of metals on heating Physics
Physics Learn EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON RESISTANCE, GSEB Physics

Temperature Coefficient of Resistance Physics Of Conductors And
Physics Learn EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON RESISTANCE, GSEB Physics
PPT Chapter 17 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6110913

How NTC Thermistors And RTDs Differ electronicsb2b

Variation of resistance of thermistor with temperature, Physics Lecture

a Variation of electrical resistance with temperature. b Frequency

Linear resistance variation with temperature for CNT grown at CH = 40
What Are Cooper Pairs & How Are They Lead To Superconductivity?

Linear Temperature Coefficient Resistor Math Encounters Blog

Typical ResistanceTemperature curve for thermistor. Download

Solved Problem (3) The variation in electrical resistance

41. Temperature dependence of the resistance of the alloys with x=13.0

20.3 Resistance and Resistivity College Physics OpenStax
But this is not true for every material i.e., all materials do not have the same dependence on temperature. The resistivities of metallic conductors within a limited range of temperature are given by the following equation: ρT= ρ0 [1 + a(T-T0)] Here, ρ T = resistivity at a temperature T. ρ 0 = resistivity at a reference temperature T 0.. Temperature effect Behavior of Insulation Resistance with variation of temperature is studied for Mineral (MgO) Insulated cable and PEEK insulated cable. Following figure shows the plot of IR of.